Unit 3
Objectives
In Unit Three, you will see the extent to which mankind goes to, to control the microbes sharing the environment.
1. Physical and Chemical Control of Microorganisms
- Terminology: Combine the prefixes “anti-” or “a-” and the suffixes “-cide” or “-static” with the following words and define each word formed: bacterio-, fungi-, viral-
- Define the following terms: sterilize, disinfect, sanitize.
- Describe the major sites of antimicrobial action.
- List physical means used to control microbial populations.
- Compare/contrast sedimentation, filtration, & centrifugation.
- Describe how each of the following factors influences antimicrobial action:
- Kind and concentration of chemical agents
- Nature and intensity of physical agents
- Time of exposure
- Number and kind of organisms present
- Temperature during exposure
- Nature of the material being exposed
- Name types of filters commonly used in microbiology.
- Describe the procedures, applications, effectiveness and mechanisms of the following antimicrobial methods:
- Pasteurization, Boiling, Tyndallization
- Autoclaving, Dry heat, low temperatures.
- Explain the process and purpose of lyophilization and desiccation.
- Compare the penetrating capacity of ultraviolet radiations with that of ionizing radiations.
- List the characteristics of an “ideal disinfectant”.
- List the groups of chemicals that are used as antimicrobials and give specific examples of each group.
- Name the gases used in sterilization and contrast their value with steam sterilization.
2. The Elements of Chemotherapy
- Cite historical landmarks in chemotherapeutic development.
- State the characteristics of an “ideal chemotherapeutic”.
- Contrast semi-synthetic and antibiotic chemotherapeutics and give examples for these categories.
- Compare/contrast broad spectrum and narrow spectrum antibiotics.
- Name several genera of microbes that are important sources of antibiotics currently used.
- List the five important actions of chemotherapeutics used today and give examples of chemotherapeutics, which have these actions.
- List the chemotherapeutics, which are used to treat tuberculosis.
- Name three antifungal chemotherapeutics.
- Describe how drug resistance develops and the resistance mechanisms used by organisms.
- List the drawbacks of chemotherapeutic usage.
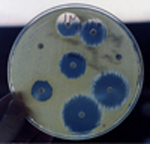
- Describe the value of susceptibility testing and tell how it is done.
Readings Talaro: Chapters 11, 12
Laboratory Activities and Objectives:
- Inoculate and interpret the results of modules that involve physical and chemical control of microorganisms.
- Inoculate and interpret the results of susceptibility testing cultures.
- Complete the activities and objectives associated with Modules.
- Perform and interpret other laboratory activities assigned.
© 2015 George Wawrzyniak. All Rights Reserved.
|