Unit 6
Objectives
In this unit we will study the pathogenic fungi that cause disease, parasites that use humans as their definitive hosts and viruses that afflict.
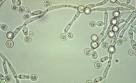
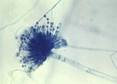
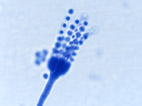
Mycology
- Compare/contrast the fungi with other organisms.
- Classify fungi based on reproduction and pathological properties.
- Describe the conditions that promote growth of fungi.
- Compare/contrast the agent, location, symptoms, treatment, and unique characteristics of the following systemic mycoses:
- North American Blastomycosis
- Coccidioidomycosis
- Histoplasmosis
- South American Blastomycosis
- Candidiasis
- Cryptococcosis
- Compare/contrast the agent, location, symptoms, treatment, and unique characteristics of the following subcutaneous mycoses:
- Sporothrix schenckii
- Chromoblastomycosis
- Mycetoma
- Identify the spread, symptoms and treatment of the following cutaneous mycoses (Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton):
- Tinea capitis
- Tinea cruris
- Tinea barbae
- Tinea pedis
- Tinea corporis
- Tinea unguium
- Identify the spread, symptoms and treatment of the following superficial mycoses:
- Identify the spread, symptoms and treatment of the following opportunistic mycoses:
- Pneumocystis pneumonia
- Zygomycosis
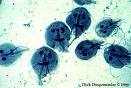
Parasitology
- Distinguish between Protozoans and Metazoans.
- Characterize the Protozoans based on motility. List the identifying Phylum characteristics of the protists that are parasites of man.
- Explain the significance of both the cyst and trophozoite stages of protozoans.
- Distinguish intermediate host from definitive host and ova (egg) from larva.
- For each of the protozoan and metazoan diseases discussed:
- Match both scientific and common names of the parasite.
- List distinguishing characteristics of the etiological agent.
- Explain ways in which the disease is transmitted and how transmission can be prevented.
- Indicate any reservoirs of infection.
- List key symptoms of the disease.
- Indicate classes of chemotherapeutics suitable for treatment.
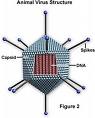
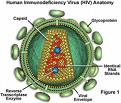
Virology
- For the viral diseases discussed identify the:
- Causative agent
- Disease caused
- Portal of entry
- Symptoms
- Transmission/prevention
- Reservoirs
- Predisposing conditions
- Status of vaccines/treatments
Readings TALARO: Chapters 22, 23, 24, 25
Laboratory Activities and Objectives:
- Complete Lab as directed.
- Identify lab specimens from Modules
|